Fraunhofer IMWS / 2025
Protection concept for renewable energies: New solutions for safe IGBT/SiC inverters
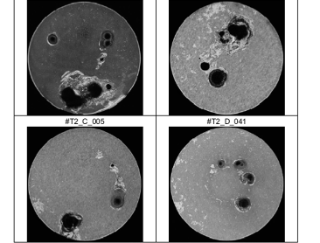
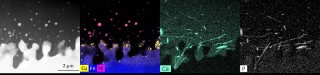
Failures in modern energy systems generate extreme short-circuit currents. Conventional shutdown methods are often no longer able to adequately protect new types of systems with semiconductor inverters and high power density. The GreenGridGuard project has developed an innovative, semiconductor-based protection concept: In the event of failure, it forces a permanent short circuit in less than 1 millisecond, safely switches off the inverter, and prevents plasma leaks. This improves protection and grid connection. The Fraunhofer Institute for Microstructure of Materials and Systems IMWS contributed its expertise in materials diagnostics and method development for new power electronics solutions.
more info